Macular Pucker (or Epi-Retinal Membrane)
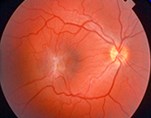 The macula is the central area of the retina that allows you to see fine details clearly. This tissue is necessary to convert the light rays that enter your eye in signals that are sent through your optic nerve to the brain to be seen as images.
The macula is the central area of the retina that allows you to see fine details clearly. This tissue is necessary to convert the light rays that enter your eye in signals that are sent through your optic nerve to the brain to be seen as images.
Damage or distortion of this important tissue causes blurred vision, making it difficult to perform tasks both at near and far like reading and driving.
What is an epi-retinal membrane?
Your eye is filled with a gel-like substance called the vitroues. This vitreous lies in front of the macula. The macula normally lies flat against the back of the eye, like film in the back of a camera. As you age, the vitreous gel shrinks, pulling away from the macula, causing separation to occur from the retina without any negative effect on your retina other than some new floaters. However, in some cases scar tissue develops on the macula. This scar tissue, sometimes called fibrosis, can warp and shrink, causing the retina to wrinkle or bulge. It is this 'wrinkling' process that has lead some doctors to call this process a 'wrinkle' in your retina when describing it to patients.
What are the symptoms of an epi-retinal membrane?
 Symptoms of macular pucker range from mild to severe and may involve one or both eyes. Symptoms occur that include:
Symptoms of macular pucker range from mild to severe and may involve one or both eyes. Symptoms occur that include:
- blurred central vision
- distorted or 'wavy' vision
- difficulty with reading or driving due to distortion of central vision
- in severe cases a central blind spot.
Remember, if the macula is the only tissue involved, you do not lose your vision completely. The only area of vision affected by this disease is the central vision, so your side vision would remain intact unless you have other eye disease affecting it.
What tests will be performed by my Doctor to diagnose and treat an epi-retinal membrane?
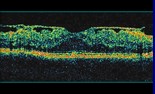
Your ophthalmologist at Kaufman Eye Institute will diagnose an epi-retinal membrane by looking inside your eye with special lenses at a biomicroscope. At that time he will order an Ocular Coherence Tomography (OCT), to scan and examine your retina. OCT uses light waves to reveal specific layers of the retina. Sometimes a fluorescein angiography is run to look for leakage in or around the retina.
How is an epi-retinal membrane treated?
For mild symptoms, no treatment is necessary. Updating your eyeglasses to the best prescription can help minimize your symptoms. Eyedrop or laser surgery does not help this visual condition.
For more severe cases, a surgery called vitrectomy is recommended. This surgery is usually done as an outpatient procedure in an operating room. During this delicate surgery Dr. Lee will use delicate instruments to remove the wrinkled tissue on your macula. After the scar tissue is removed, the macula will flatten over time and the vision will slowly improve. Surgery should be considered carefully by you and your ophthalmologist.


